Feedback Mechanism
Table of content
- Introduction to Feedback Mechanisms
- Types of Feedback Mechanisms
- Benefits of Feedback Mechanisms
- Importance of Effective Feedback
- Examples of Feedback Mechanisms
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction to Feedback Mechanisms:
In any organization, whether it is a business, non-profit, or government agency, feedback is an essential component of success. Feedback mechanisms provide a way for individuals or groups to receive information about their performance, behavior, or other aspects of their work. This information can then be used to improve performance and achieve better results. In this article, we will explore different types of feedback mechanisms, their benefits, and the importance of effective feedback in maximizing success.
Types of Feedback Mechanisms:
There are several types of feedback mechanisms, including verbal, written, formal, and informal feedback. Verbal feedback is given through face-to-face communication, while written feedback can be in the form of emails, memos, or performance evaluations. Formal feedback is typically given through a structured process, such as an annual performance review, while informal feedback can be given on an ongoing basis through conversations or meetings.
Another type of feedback mechanism is 360-degree feedback, which involves gathering feedback from multiple sources, including peers, supervisors, and subordinates. This type of feedback provides a more comprehensive view of an individual's performance and can help identify areas for improvement.
Benefits of Feedback Mechanisms:
Effective feedback mechanisms have several benefits, including increased productivity, higher morale, and better communication. Feedback can help individuals understand their strengths and weaknesses and identify areas where they need to improve. This can lead to increased productivity and better performance.
Feedback mechanisms can also improve morale by showing employees that their contributions are valued and that their efforts are noticed. When employees feel valued, they are more likely to be engaged and motivated in their work.
Feedback mechanisms can also improve communication within an organization. By providing feedback on a regular basis, individuals can learn how to communicate more effectively and work collaboratively with others.
Importance of Effective Feedback:
Effective feedback is essential for maximizing success in any organization. When feedback is delivered in a constructive and timely manner, individuals are more likely to take action to improve their performance. Feedback can also help individuals feel more confident in their abilities and develop a growth mindset.
On the other hand, ineffective feedback can have negative consequences, such as decreased morale and increased turnover. The feedback that is delivered in a harsh or critical manner can lead to defensiveness and resistance to change. It is important to deliver feedback in a way that is respectful and encourages growth.
Examples of Feedback Mechanisms:
There are many different ways to implement feedback mechanisms in an organization. Some common examples include:
- Performance evaluations: This is a formal process where an employee's performance is evaluated based on specific criteria, such as job duties and goals.
- One-on-one meetings: These are informal meetings between a supervisor and an employee where feedback can be given on an ongoing basis.
- 360-degree feedback: This is a process where feedback is gathered from multiple sources, including peers, supervisors, and subordinates.
- Customer feedback: This can be gathered through surveys or other methods to gather feedback on products or services.
- Team meetings: These meetings can provide an opportunity for team members to give feedback to each other and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Feedback mechanisms are a crucial component in achieving success within any organization. By providing regular feedback through various methods such as performance evaluations, one-on-one meetings, or customer feedback, individuals can identify their strengths and weaknesses and make improvements where needed.
Effective feedback can lead to increased productivity, higher morale, and better communication, while ineffective feedback can have negative consequences. To implement an effective feedback mechanism, it is important to establish clear goals, create a culture that values feedback, and provide training on how to deliver feedback effectively. By maximizing the benefits of feedback mechanisms, organizations can improve their overall performance and achieve greater success.
FAQs
What Is a Positive And Negative Feedback Mechanisms?
Positive and negative feedback mechanisms are two types of control mechanisms that occur in biological systems to maintain homeostasis, which is the stable internal environment necessary for an organism to function properly.
Positive feedback is a mechanism in which a change in a system leads to an amplified response, which further increases the change in the system. This can result in a runaway effect and can cause the system to move further away from its original state. An example of positive feedback is the release of oxytocin during childbirth. The contractions of the uterus stimulate the release of oxytocin, which causes the contractions to become stronger and more frequent, leading to the eventual birth of the baby.
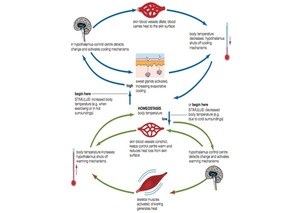
Negative feedback is a mechanism in which a change in a system leads to a response that counteracts the change, bringing the system back to its original state. This helps to maintain stability in the system and prevent it from moving too far away from its optimal state. An example of negative feedback is the regulation of body temperature. When the body temperature rises, the blood vessels in the skin dilate, allowing heat to escape. At the same time, sweat glands are activated, which leads to evaporation of sweat and further cooling of the body. This helps to bring the body temperature back to its optimal level.
What Are The Stages Of The Feedback Mechanism?
The stages of a feedback mechanism generally include the following:
Stimulus: This is the initial change or disturbance in the system that triggers the feedback mechanism. For example, in the case of body temperature regulation, an increase in body temperature would be the stimulus.
Receptor: This is the part of the system that detects the change in the stimulus. In the body temperature regulation example, the temperature sensors in the skin and brain would act as receptors and detect the increase in body temperature.
Control center: This is part of the system that processes the information received from the receptors and determines the appropriate response. In the body temperature regulation example, the hypothalamus in the brain would act as the control center.
Effector: This is the part of the system that carries out the response determined by the control center. In the body temperature regulation example, the sweat glands and blood vessels in the skin would act as effectors and help to reduce body temperature.
Response: This is the result of the action taken by the effectors, which helps to bring the system back to its optimal state. In the body temperature regulation example, the response would be a decrease in body temperature.
Feedback: This is the information that is sent back to the control center to indicate whether the response was successful in restoring the system to its optimal state. In the body temperature regulation example, feedback could come from the temperature sensors in the skin and brain, which would indicate whether body temperature has been restored to the optimal level.
What Is An Example Of Positive And Negative Feedback In Physiology?
An example of positive feedback in physiology is the process of blood clotting. When there is an injury to a blood vessel, platelets in the blood are activated and begin to clump together at the site of the injury, forming a plug. The platelets then release chemicals that attract more platelets to the site, leading to further clotting and amplification of the response. This positive feedback loop continues until a clot is formed, which helps to stop bleeding.
An example of negative feedback in physiology is the regulation of blood glucose levels. When blood glucose levels rise after a meal, the pancreas releases insulin, which signals the body's cells to take up glucose from the blood and use it for energy. This lowers blood glucose levels, which in turn reduces insulin secretion. If blood glucose levels fall too low, the pancreas releases glucagon, which signals the liver to release stored glucose into the blood, raising blood glucose levels back to the optimal range. This negative feedback loop helps to maintain stable blood glucose levels in the body.
What Is A Good Example Of Positive Feedback?
A good example of positive feedback is the process of childbirth. During labor, the uterus contracts to push the baby through the birth canal. As the baby's head pushes against the cervix, it sends a signal to the brain to release the hormone oxytocin. Oxytocin causes the uterine contractions to become stronger and more frequent, which in turn pushes the baby's head further down onto the cervix. This pressure on the cervix causes more oxytocin to be released, which leads to even stronger contractions and further pressure on the cervix. This cycle of positive feedback continues until the baby is born.
In this example, the initial stimulus (pressure on the cervix) leads to an amplified response (increased oxytocin release and stronger uterine contractions), which further increases the pressure on the cervix, leading to a stronger response. This positive feedback loop continues until the baby is born, which is the end result of the process.
What Is An Example Of A Negative Feedback Mechanism?
An example of a negative feedback mechanism is the regulation of body temperature in mammals. When the body temperature rises above the normal range, the thermoreceptors in the skin and brain detect the increase and send signals to the hypothalamus, which acts as the body's control center for temperature regulation.
The hypothalamus then triggers the appropriate response to reduce body temperature, which includes the dilation of blood vessels in the skin to increase heat loss through radiation and sweating to increase heat loss through evaporation. As body temperature begins to decrease toward the normal range, the thermoreceptors send feedback signals to the hypothalamus to reduce the response and maintain the body temperature within the normal range.
This negative feedback mechanism helps to maintain a stable body temperature in the face of external changes in temperature or internal heat production.
Why Is It Called A Negative Feedback Mechanism?
It is called a negative feedback mechanism because the response to the initial stimulus serves to reduce or oppose the magnitude of the stimulus. In other words, the feedback response acts in a negative direction relative to the initial stimulus.
In a negative feedback mechanism, the system is continuously monitored for changes from a desired or set point, and the system responds by counteracting those changes to bring the system back toward the set point. This helps to maintain the stability and homeostasis of the system.
In contrast, a positive feedback mechanism amplifies or reinforces the initial stimulus, leading to an even greater response. In positive feedback, the feedback response acts in the same direction as the initial stimulus, leading to a self-perpetuating cycle of increasing response.
Is Blood Clotting Positive Or Negative Feedback?
Blood clotting is an example of a positive feedback mechanism. When a blood vessel is injured, platelets in the blood are activated and begin to clump together at the site of the injury, forming a plug. The platelets then release chemicals that attract more platelets to the site, leading to further clotting and amplification of the response.
This positive feedback loop continues until a clot is formed, which helps to stop bleeding. The initial stimulus (injury to a blood vessel) leads to an amplified response (platelet aggregation and chemical release), which further increases the response, leading to the formation of a clot. This positive feedback loop continues until the clot is formed, which is the end result of the process.
So, blood clotting is an example of a positive feedback mechanism.
What Are Two Types Of Feedback Mechanisms?
The two types of feedback mechanisms are positive feedback and negative feedback.
Positive feedback occurs when a response amplifies the initial change or stimulus, leading to an even greater response. In positive feedback, the feedback response acts in the same direction as the initial stimulus, leading to a self-perpetuating cycle of increasing response.
Negative feedback occurs when a response counteracts the initial change or stimulus, leading to a reduction or reversal of the response. In negative feedback, the feedback response acts in the opposite direction to the initial stimulus, leading to a stabilization or homeostasis of the system.
Why Is A Feedback Mechanism Important?
Feedback mechanisms are important because they help to maintain stability and homeostasis in biological systems. Biological systems are complex and are constantly subjected to various internal and external stimuli that can disrupt their normal functioning. Feedback mechanisms help to monitor and respond to these changes, maintaining stability and restoring balance to the system.
For example, in the human body, the regulation of blood glucose levels, body temperature, and blood pressure are all examples of feedback mechanisms that help to maintain homeostasis. Without these feedback mechanisms, the body would be unable to respond to changes in these parameters, leading to potentially harmful consequences.
Feedback mechanisms are also important in other fields such as engineering, control systems, and economics. In engineering, feedback mechanisms are used to regulate and stabilize various systems, such as in the control of temperature or speed of a motor. In economics, feedback mechanisms are used to adjust production levels, prices, and other variables to maintain equilibrium in a market.
Is Menstruation Negative Feedback?
Menstruation is not an example of negative feedback, but rather a cyclic process that occurs in response to hormonal changes in the body.
During the menstrual cycle, the levels of hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, fluctuate in a specific pattern. These hormones act on the reproductive organs, causing changes in the uterine lining and the ovaries, which eventually lead to ovulation and menstruation.
The menstrual flow itself is not a feedback mechanism, but rather a consequence of the hormonal changes that occur during the menstrual cycle. However, the hormonal changes that occur during the menstrual cycle can be regulated by feedback mechanisms. For example, changes in estrogen and progesterone levels can trigger feedback mechanisms that regulate their production and release, helping to maintain homeostasis in the body.
What Are Positive Feedback Mechanisms?
Positive feedback mechanisms are feedback loops in which the response amplifies or reinforces the initial change or stimulus, leading to an even greater response. In positive feedback, the feedback response acts in the same direction as the initial stimulus, leading to a self-perpetuating cycle of increasing response.
Positive feedback mechanisms are often involved in processes that require a rapid and large response, such as in the initiation of labor during childbirth or the formation of blood clots. In these processes, a small initial stimulus triggers a cascade of events that amplify the response until the desired outcome is achieved.
An example of a positive feedback mechanism is the process of blood clotting. When a blood vessel is injured, platelets in the blood are activated and begin to clump together at the site of the injury, forming a plug. The platelets then release chemicals that attract more platelets to the site, leading to further clotting and amplification of the response.






0 Comments